In this example we demonstrate how to compute a current potential on one surface that minimizes the error of the normal magnetic field on another. This is relevant to stellarator optimization when the normal field is minimized on a desired plasma surface and the current potential lies on a so-called winding surface here coils will be initialized for further optimization.
- Note
- Running this example requires the h5py python package, which is installable using
pipor other standard methods.
Load ThinCurr library
To load the ThinCurr python module we need to tell python where to the module is located. This can be done either through the PYTHONPATH environment variable or within a script using sys.path.append() as below, where we look for the environement variable OFT_ROOTPATH to provide the path to where the OpenFUSIONToolkit is installed (/Applications/OFT for binaries on macOS).
Generate mesh and ThinCurr input for coil and plasma surfaces for NCSX
First we create ThinCurr models for the winding and plasma surfaces using a REGCOIL definition of the NCSX stellarator using build_regcoil_grid(). This subroutine builds a uniform grid over one field period, which can then be used by build_periodic_mesh() to build a mesh from the resulting grid. The result is a ThinCurr model, including periodicity mapping information (r_map).
Plot resulting winding surface mesh
Plot resulting plasma surface mesh
Save models to HDF5 format
Saving mesh: thincurr_plasma.h5 Saving mesh: thincurr_coil.h5
Compute optimal winding surface current
Setup ThinCurr model for winding surface
We now create a ThinCurr instance for the winding surafce. Once created, we setup the model from the existing HDF5 mesh definition generated above using setup_model(). We also initialize I/O for this model using setup_io() to enable output of plotting files for 3D visualization in VisIt or Paraview.
In this case we specify a coil directory to use for saving I/O files to keep things separate for the other cases to be run in this notebook and in ThinCurr Python Example: Compute frequency-response in a torus.
- Note
- A warning will be generated that no XML node was found and a default resistivity value is being used. This is OK as we will not use the resitivity matrix with this model.
#---------------------------------------------- Open FUSION Toolkit Initialized Development branch: main Revision id: 8440e61 Parallelization Info: Not compiled with MPI # of OpenMP threads = 4 Fortran input file = oftpyin XML input file = none Integer Precisions = 4 8 Float Precisions = 4 8 16 Complex Precisions = 4 8 LA backend = native #---------------------------------------------- Creating thin-wall model Orientation depth = 24192 Loading V(t) driver coils Loading I(t) driver coils # of points = 12096 # of edges = 36288 # of cells = 24192 # of holes = 4 # of Vcoils = 0 # of closures = 0 # of Icoils = 0 Building holes WARNING: Unable to find "thincurr" XML node WARNING: No "thincurr" XML node, using "eta=mu0" for all regions
Setup ThinCurr model for plasma surface
We now create a ThinCurr instance for the winding surafce. Once created, we setup the model from the existing HDF5 mesh definition generated above using setup_model(). We also initialize I/O for this model using setup_io() to enable output of plotting files for 3D visualization in VisIt or Paraview.
In this case we specify a plasma directory to use for saving I/O files to keep things separate for the other cases to be run in this notebook and in ThinCurr Python Example: Compute frequency-response in a torus.
- Note
- A warning will be generated that no XML node was found and a default resistivity value is being used. This is OK as we will not use the resitivity matrix with this model.
Creating thin-wall model Orientation depth = 24576 Loading V(t) driver coils Loading I(t) driver coils # of points = 12288 # of edges = 36864 # of cells = 24576 # of holes = 2 # of Vcoils = 0 # of closures = 0 # of Icoils = 0 Building holes WARNING: Unable to find "thincurr" XML node WARNING: No "thincurr" XML node, using "eta=mu0" for all regions
Compute mutual inductance between coil and plasma surfaces
Building element<->element mutual inductance matrix
Time = 1m 9s
Compute coil current regularization matrix
1.2828298118544255
Compute optimal current distribution with specified regularization
Save error and current distribution for plotting
Removing old Xdmf files Creating output files Removing old Xdmf files Creating output files
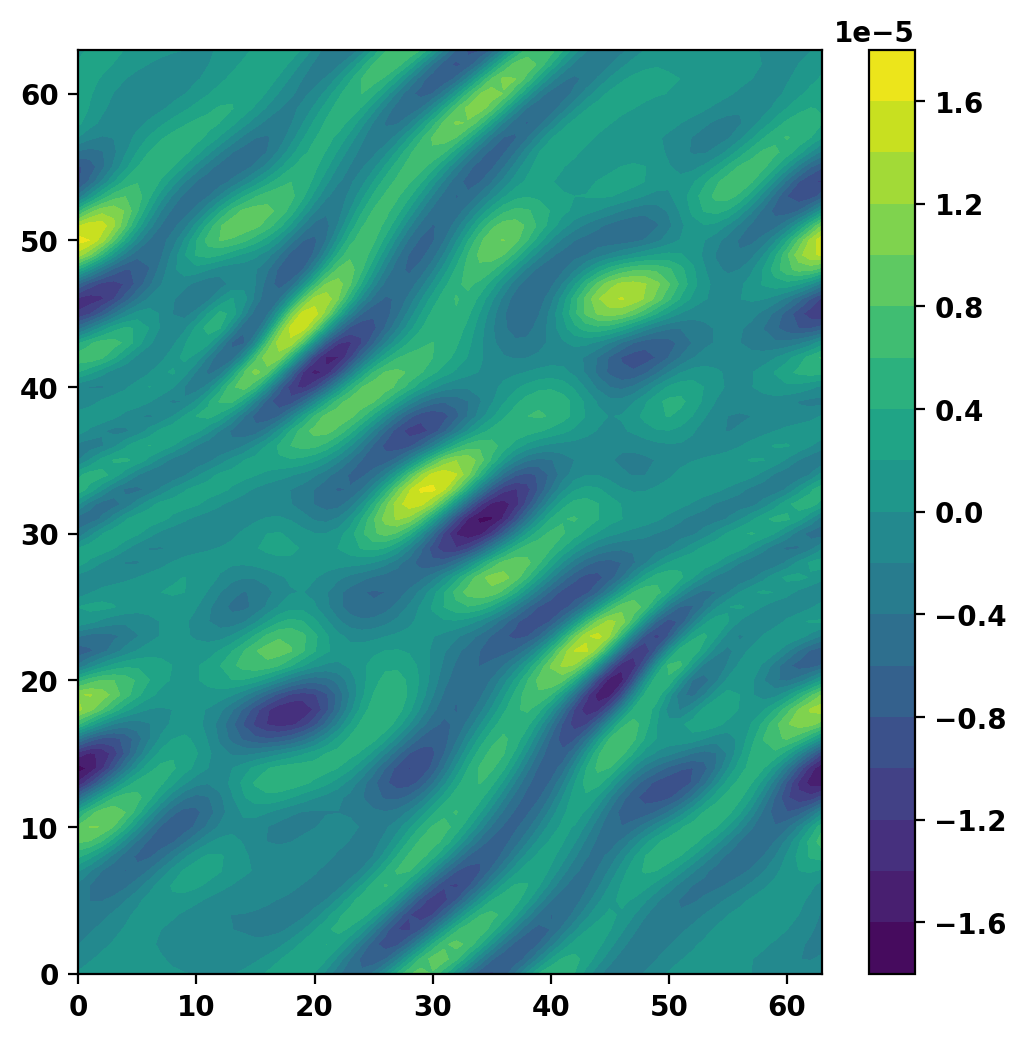
Plot current potential on one field period
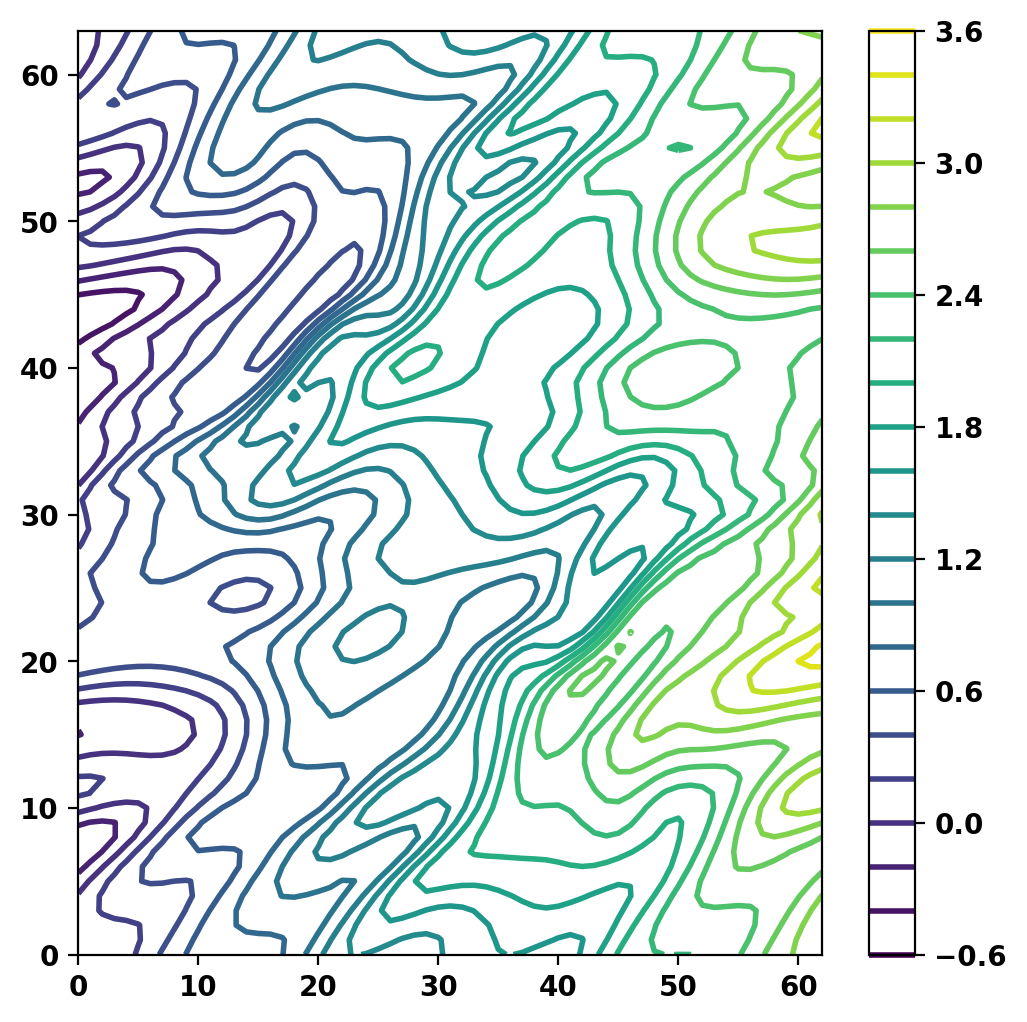
Plot normali field error on one field period